RESEARCH
GPCR

The most proven family of target molecules in genomic drug discovery and the one that many researchers and companies are working on are drug receptors, represented by G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), which are sensor molecules that are responsible for transmitting information into the cell through their conjugation with G proteins. GPCRs are also often associated with disease and are among the primary targets for drug development. However, in many of these cases, the substance (ligand) that acts upon conjugation is unknown (called orphan receptors), and the physiological phenomena involved in GPCRs remain unresolved.
We have searched for orphan receptor ligands and identified a novel fatty acid receptor, GPR120 (FFAR4). We further showed that this GPR120 promotes the secretion of peptide hormones such as GLP-1 upon dietary fatty acid stimulation and is associated with obesity in both mice and humans. These results indicate that GPR120 may be a potential therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome.
Our laboratory is conducting research on fatty acid receptors represented by GPR120 with the goal of rapidly identifying the target molecules involved in the disease and elucidating their physiological roles.
Virtual Screening
In drug discovery research, searching for target ligands is beneficial not only for new drug candidates, but also for elucidating the physiological function and structure of the target. However, screening a large number of compounds is not realistic from the viewpoint of resources and cost. Therefore, we use docking simulation and modeler dymanics to predict the activity of compounds.
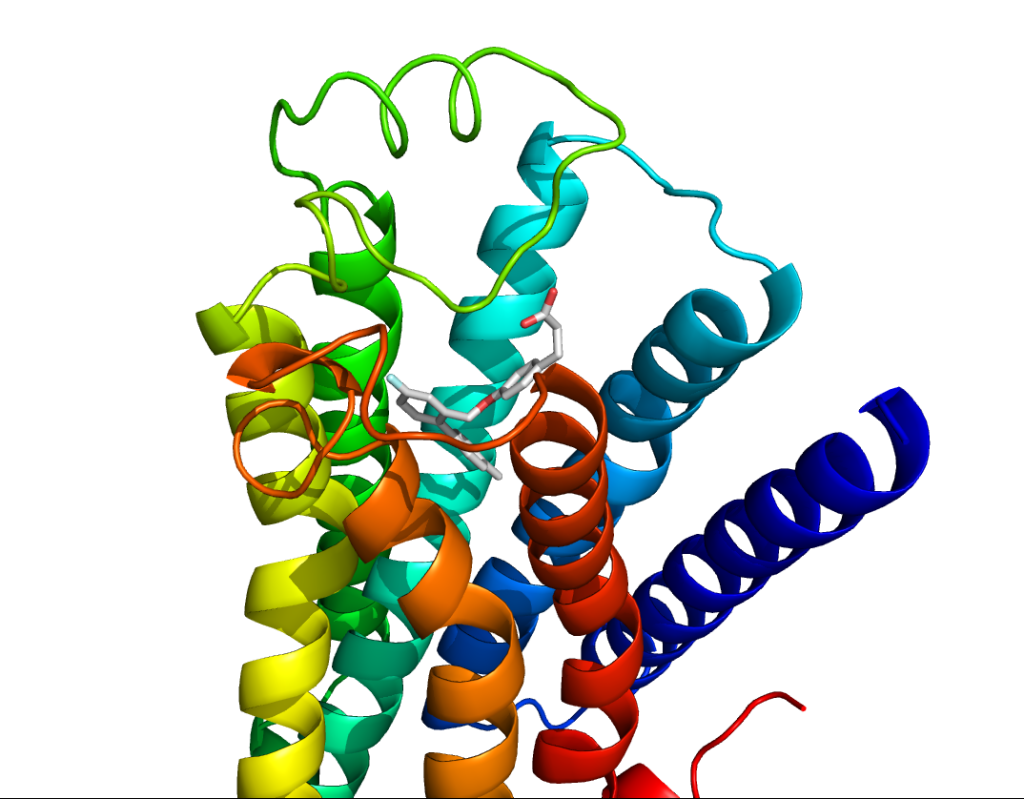
Gene expression analysis

One of the most important aspects of genomic drug discovery is the determination of drug target molecules. Microarray (DNA chip) and RNA sequencing analysis can identify specific gene expression patterns (profiles) for pathological conditions and comprehensively analyze all transcripts in cells (transcriptome analysis) based on these profiles, enabling the discovery of unknown genes, elucidation of regulatory mechanisms of gene expression, and rapid discovery of drug development targets. This enables the discovery of unknown genes, the elucidation of regulatory mechanisms of gene expression, and the rapid discovery of targets for drug development.
By analyzing the data obtained using microarrays and RNA sequencing and creating a database of the results, it is expected to be possible to narrow down the group of genes related to diseases and therapies through biological verification and to conduct cell biological function analysis targeting the related genes and to select small molecule compounds. The results of this study will be used for the development of a new drug candidate for the treatment of cancer.